The Major Body Space in Arthropods Is the
What type of major body space do members of the Phylum Arthropoda present. Hemocoel Molting and subsequent ecdysis in crustaceans involves a molt-inhibiting hormone produced by the X-organ of the eye stalk and a molting hormone produced by the Y-organs near the mandibles.
Arthropod Morphology Parts Of A Grasshopper Amnh
The basic body plan of arthropods.

. They are all extinct. Each body segment may bear a pair of jointed appendages. Arthropods are unusual among invertebrates.
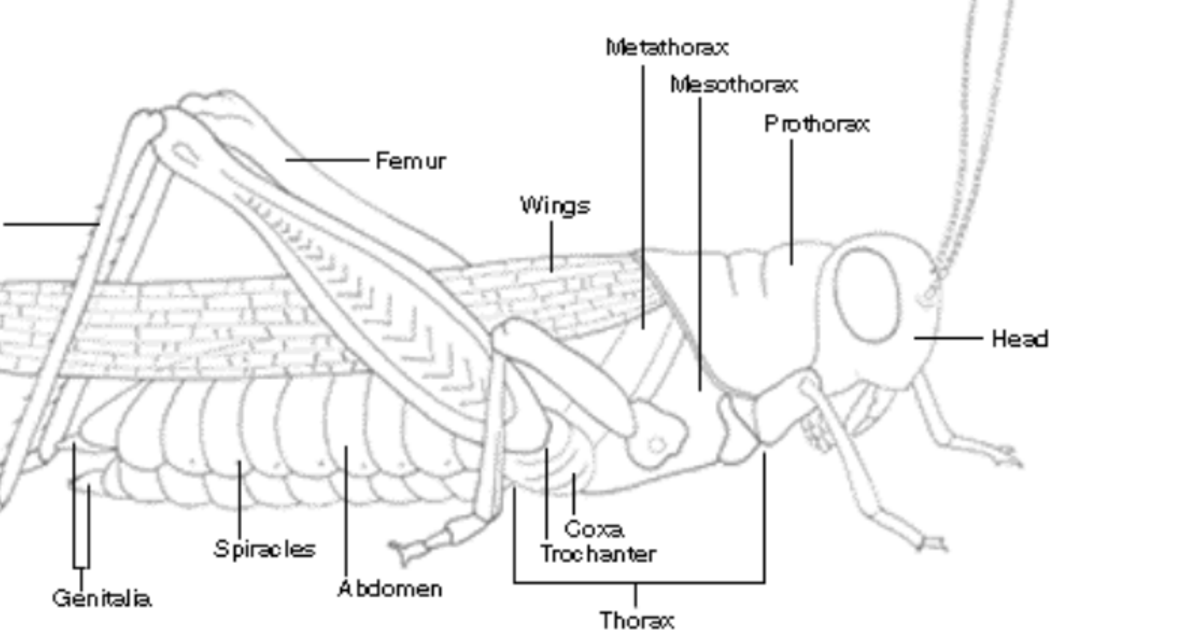
There are head and trunk thorax plus abdomen. Know the major groups of arthropods below and how they differ in terms of habitat body regions or body segmentation and number of walking legs. All of the choices listed are crayfish appendages.
The neuromuscular organization of arthropods is quite different from that of. In organisms like spider or scorpion. The major body space in arthropods is the pseudocoelom.
Body Cavity of Arthropods. Ventral means in front so this means that arthropods nervous systems run along the front of their bodies near their stomachs instead of along their backs like the spinal cords of animals. In crayfish a protective carapace covers the head and thorax which are collectively referred to as the cephalothorax.
An upper and a lower pair. Two body parts - consist of an abdomen posterior part of the body and a cephalothorax which is the anterior part of the body. Trilobites exist today as fossils only.
In organisms like centipede and millipede. Body regions of arthropod organisms are. A head thorax and abdomen as shown on this insect.
The respiratory apparatus of a crayfish is. In most terrestrial arthropods such as insects and spiders the epicuticle contains waxes that aid in reducing evaporative water loss. Identification of Insects and their Relatives.
Behind the bases of the antennae and extended over the mouth is a median lobe Lm such as all arthropods have and which is commonly known as the labrum though students of trilobites have generally called it the hypostome. Cuticle body segmentation body cavity appendages Be able to decribe the molting procedure and the role that it plays in the life of arthropods. The body of crustaceans is divided into three regions the head thorax and abdomen.
The system is similar to that of annelid worms from which arthropods may have evolved. The major body space in arthropods that is not a coelom but a persistent blastocoel that becomes blood-filled hemocoel Subphylum Crustacea Antennal glands. Practice Arthropod Structure and Function.
Maxillaey or green glands that open at the anterior end Subphylum Crustacea Statocyst. The arthropod nervous system consists of a dorsal brain and a ventral ganglionated longitudinal nerve cord primitively paired from which lateral nerves extend in each segment. There are prosoma head plus thorax and opisthosoma abdomen.
The procuticle consists of an outer exocuticle and an inner endocuticle. Given that arthropods are characterized by a fusion and reduction in segments why do you think. It is called mixocoel and as blood flows through it this is also referred to as haemocoel.
They lack locomotory cilia even as larvae. Hemocoel In arthropods the hemocoel is filled with what. Originally it seems that each appendage-bearing segment had two separate pairs of appendages.
All arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and possess a segmented body covered by an exoskeleton containing chitin which serves as both armour and a surface for muscle attachment. There are cephalothorax head plus thorax and abdomen. This process of segment fusion or tagmosis usually results in an arthropod body that consists of three major sections a head thorax and abdomen.
Arthropod segments have also fused together into functional units called tagma. Arthropods also have two body elements that are not part of this serially repeated pattern of segments an acron at the front ahead of the mouth and a telson at the rear behind the anus. All arthropods posses an exoskeleton bi-lateral symmetry jointed appendages segmented bodies and specialized appendages.
At the junction or joints between the plates and cylinders the exoskeleton is thin. In Arthropoda true coelom appears as pouches in the embryonic stage In course of development its walls are used up in the formation of organs and the space becomes continuous with the blastocoel. The exoskeleton is composed of a thin outer protein layer the epicuticle and a thick inner chitinprotein layer the procuticle.
The phylum includes carnivores herbivores omnivores detritus feeders filter feeders and parasites. Arthropods have three primary body segments tough exoskeletons and an open circulatory system. This indicates how strong in your memory this concept is.
The cephalothorax is composed of two the dorsal carapace and the ventral sternum. Blood called hemolymph fills the sinuses in the tissues which comprise part of the open circulatory system What class of arthropods are all extinct. The problem that a rigid external covering imposes on movement has been solved by having the exoskeleton divided into plates over the body and through a series of cylinders around the appendages.
The eyes are mounted on the acron. The abdomen is segmented and flexible. The major arthropod classes can be separated by comparing their number of body regions legs and antennae.
Chelicerates myriapods crustaceans insects. Body segmentation is seen elsewhere in the Animal Kingdom. Insects are part of the phylum of animals called Arthropoda.
Among living arthropods the millipedes most closely suggest what the ancestral arthropod might have looked like. Trilobita marine arthropods that lived 542-251 million years ago. The major body space in arthropods is the hemocoel The majority of insects feed on plant juices and tissues sea anemones and corals lack a medusa stage snails that lack gills are called pulmonate and their mantle cavity functions.
The mouth presumably is covered by the labrum and behind it is a small metastomal lobe.

Insect Definition Characteristics Types Classification Facts Insect Species Insects Arthropods

No comments for "The Major Body Space in Arthropods Is the"
Post a Comment